Services
Medial Branch Block Injections
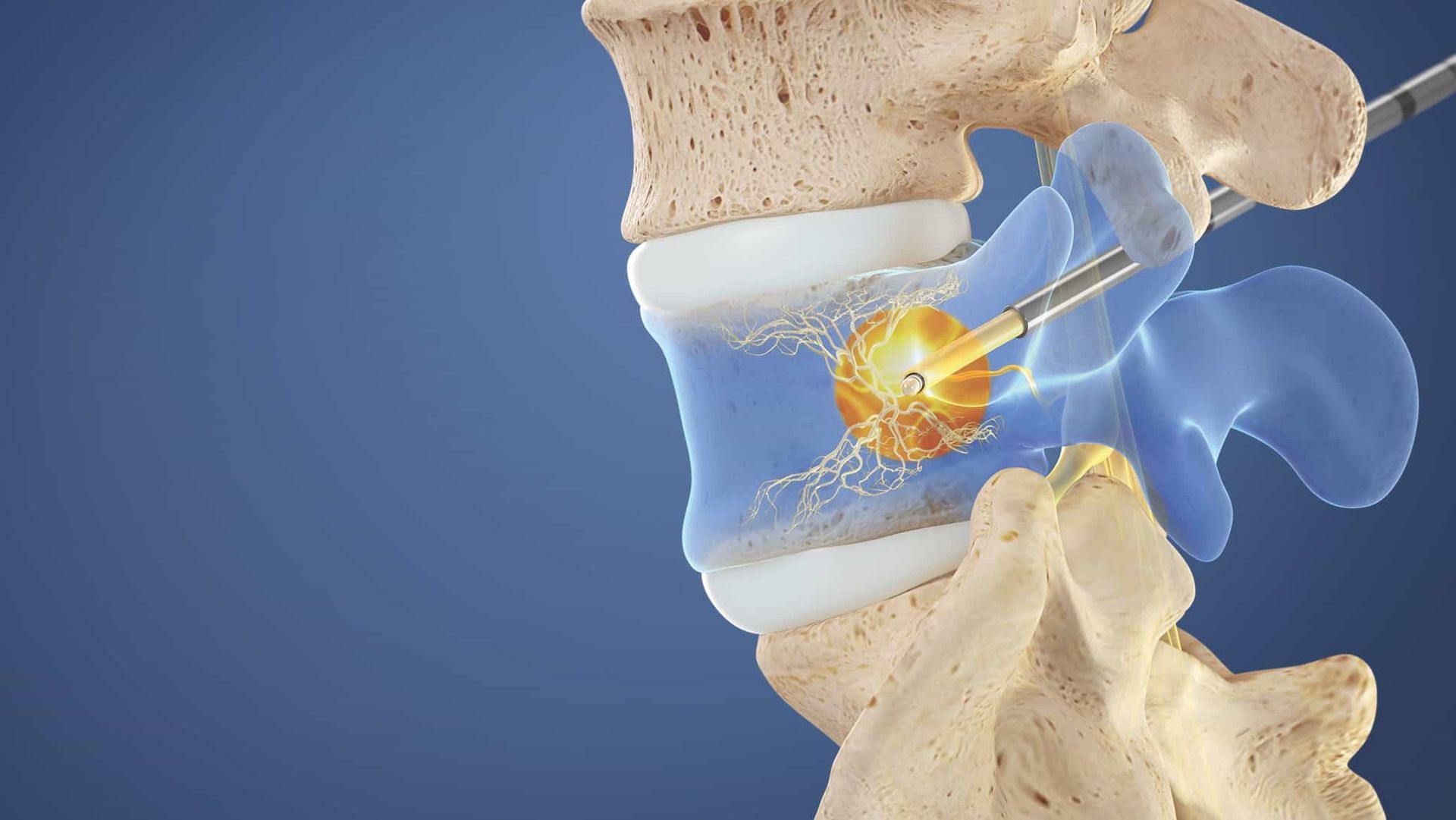
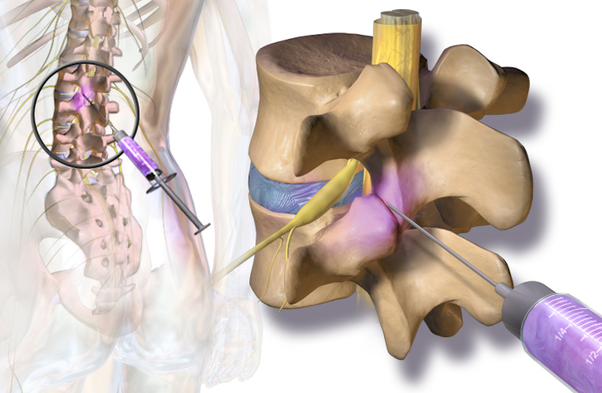
A medial branch block is an image guided, minimally invasive method of targeted drug therapy which is performed for diagnostic purposes to confirm that the facet joints (joints in the back of the spine) are the source of your pain. Typically a medial branch block is performed twice (two separate occasions) to optimize our certainty of the diagnosis. If the blocks are positive then you may be a candidate for a procedure called a radiofrequency ablation which can provide long lasting (often 6+ months) of benefit. This procedure can be performed for the neck and the back.
After the procedure is performed it is VERY important that you monitor how your pain compares to your typical pain so that you can tell your provider at the next visit. To help you remember you will be provided a pain diary to fill out following the procedure. It is important to note that this is a DIAGNOSTIC procedure and you should not expect long lasting benefits (generally no more than a few hours). It is also important to know that this procedure typically only addresses pain that stays in the neck or back and is not likely to improve pain that radiates down your arms or legs.
How is a medial branch block injection performed?
Patient Positioning
The patient lies face down.
Tissue Anesthetized
A local anesthetic (typically lidocaine) is used to numb the skin.
Fluoroscopic Guidance
Using a fluoroscope for guidance (live x-ray guidance), the physician directs the needles to the areas where the medial branch runs towards the suspected problematic joints. The physician uses the fluoroscope to confirm the correct location of the needle tip.
Medication Injected
A local anesthetic is injected around the medial branch nerve which should prevent transmission of pain signals from the joint from reaching the brain for the duration that the anesthetic lasts.
End of Procedure
The needles are removed and a small bandage is applied to cover the tiny needle surface wound.
How long does it take for the medial branch block to work?
Typically the local anesthetic takes effect over the course of a few minutes and frequently you will be able to notice a difference in your symptoms as you get up off of the procedure table. As discussed above, this is a diagnostic procedure and is only expected to last for the duration of the local anesthetic.
Who performs a medial branch block injection?
Medial branch block injections are performed by one of the board certified interventionalists at Spine & Nerve Diagnostic Center (SNDC). Our interventionalists have performed thousands of these procedures.
Where are branch block injections performed?
Medial branch block injections are typically performed at our state of the art SNDC procedure suites.